Introduction
Have you ever wondered how your favorite video games or movies create those incredibly realistic 3D environments? Or how architects visualize buildings before they’re even built? The answer lies in a fascinating technology called 3D reconstruction. This process turns flat, 2D images into detailed 3D models, enabling a wide range of applications from entertainment to engineering. Let’s explore how this magic happens in a way that’s easy to understand, even if you’re not a techie.
The Basics: What is 3D Reconstruction?
At its core, 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance of real objects or scenes in three dimensions. It’s like taking a series of flat photographs and combining them to build a full 3D model that you can rotate, zoom in on, and view from different angles.
Think of it this way: when you look at a photo of a building, you only see one side. But with 3D reconstruction, you get the entire structure—every wall, window, and detail—recreated in a virtual space. This is incredibly useful in fields like architecture, gaming, and even virtual reality (VR), where understanding the full 3D shape is crucial.
The Building Blocks: How It Works
So, how do we go from a bunch of flat images to a 3D model? The magic happens through a few key steps:
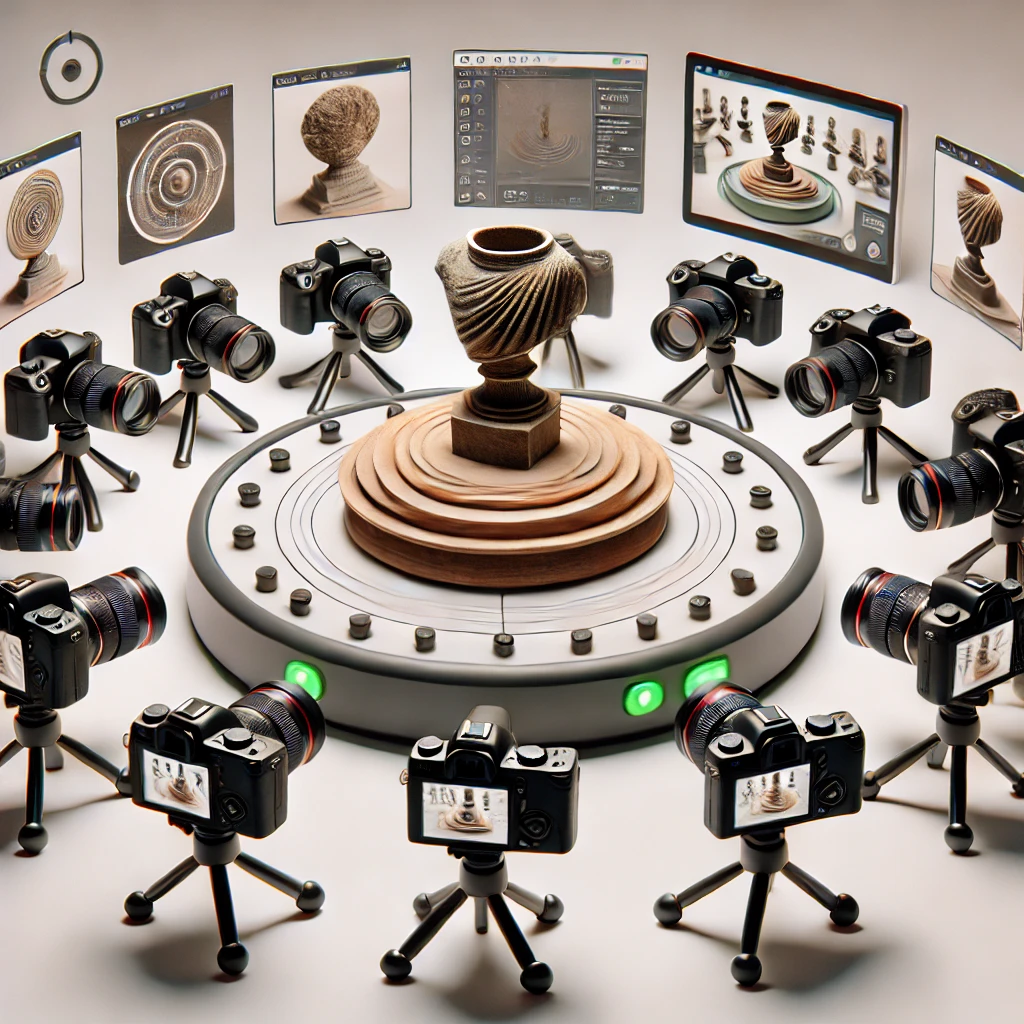
Capturing Images from Different Angles
- To reconstruct a 3D model, the first step is to take multiple photos of the object or scene from different angles. Imagine walking around a statue and snapping pictures from every side. Each photo captures a different perspective, providing the raw material needed for reconstruction.
Finding Common Points
- Once we have our photos, the next step is to find points in each image that correspond to the same physical point on the object. For instance, if there’s a distinctive mark on the object, the algorithm will identify that mark in every photo. These common points are crucial because they help the computer understand how the photos relate to each other in 3D space.
Finding Common Points
- Once we have our photos, the next step is to find points in each image that correspond to the same physical point on the object. For instance, if there’s a distinctive mark on the object, the algorithm will identify that mark in every photo. These common points are crucial because they help the computer understand how the photos relate to each other in 3D space.
Calculating Depth and Structure
- After identifying common points, the algorithm uses them to calculate the depth and structure of the object. This is where the real 3D magic happens. The computer determines how far each point is from the camera, essentially mapping out the object’s shape in three dimensions.
Creating the 3D Model
- Finally, all the depth information is combined to create a detailed 3D model. This model can be textured (adding colors and details) to look just like the real thing. Now, you’ve got a fully interactive 3D object that you can explore from any angle!

Real-World Applications
3D reconstruction isn’t just a cool tech trick—it has some seriously practical applications across various industries:
Gaming and Movies: Ever wondered how video games and CGI-heavy movies create such realistic environments? 3D reconstruction plays a huge role in bringing these digital worlds to life, allowing creators to build intricate models of everything from characters to entire landscapes.
Architecture and Construction: Architects and builders use 3D models to visualize projects before construction even begins. This helps in planning and ensures that everything fits together perfectly.
Cultural Heritage Preservation: 3D reconstruction is also used to preserve historical sites and artifacts. By creating detailed digital models, we can explore and study these treasures without causing any damage to the originals.
Medical Imaging: In healthcare, 3D models help doctors plan surgeries, visualize complex structures like blood vessels, and even create personalized implants.
The Future of 3D Reconstruction
The technology behind 3D reconstruction is constantly evolving, getting faster, more accurate, and easier to use. With advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, we’re seeing even more impressive results. Imagine a future where you can create a perfect 3D model of your living room using just your smartphone, or where virtual reality feels indistinguishable from the real world.
Conclusion
3D reconstruction is a powerful technology that’s transforming the way we see and interact with the world. Whether it’s in the entertainment industry, architecture, or medicine, the ability to turn 2D images into fully-realized 3D models opens up a world of possibilities. And the best part? As this technology continues to evolve, it’s only going to become more accessible and integrated into our everyday lives.