Applications of 3D and Volumetric Scanning in Healthcare
Introduction
The healthcare industry has always been at the forefront of adopting new technologies, and 3D and volumetric scanning are no exception. These cutting-edge tools are revolutionizing the way we diagnose, plan treatments, and even perform surgeries. Whether it’s creating detailed models of organs, customizing medical devices, or enabling more precise surgeries, 3D and volumetric scanning are making healthcare more effective and personalized. Let’s dive into how these technologies are being used to improve patient care and outcomes.
What is 3D and Volumetric Scanning?
Before we get into the applications, let’s briefly explain what 3D and volumetric scanning are. 3D scanning involves capturing the shape of an object or body part in three dimensions, creating a detailed digital model. Volumetric scanning takes this a step further by capturing not just the surface, but the entire volume of an object, including its internal structures. This creates a complete 3D representation that can be examined from any angle and sliced through virtually.
These technologies are incredibly useful in healthcare because they allow doctors to see and understand the human body in ways that were never possible before.
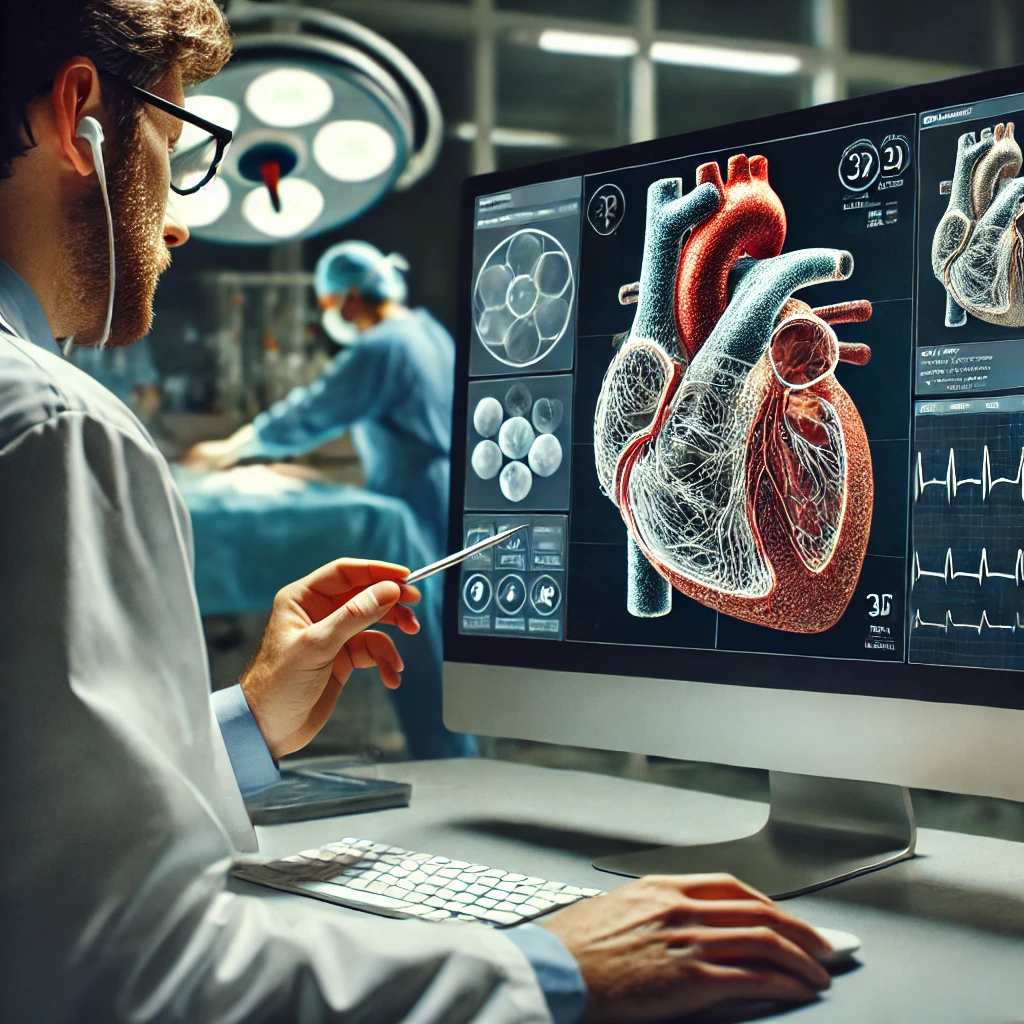
1. Precision Surgery Planning
One of the most impactful uses of 3D and volumetric scanning in healthcare is in planning surgeries. Surgeons can use these detailed scans to create a 3D model of a patient’s anatomy, allowing them to plan the procedure with incredible precision. For example, in complex surgeries like brain or heart surgery, doctors can use these models to identify the best approach, avoid critical structures, and reduce the risk of complications.
This technology also enables virtual surgery simulations, where surgeons can practice the procedure on a virtual model before performing it on the patient. This not only improves the success rate but also shortens the actual surgery time.
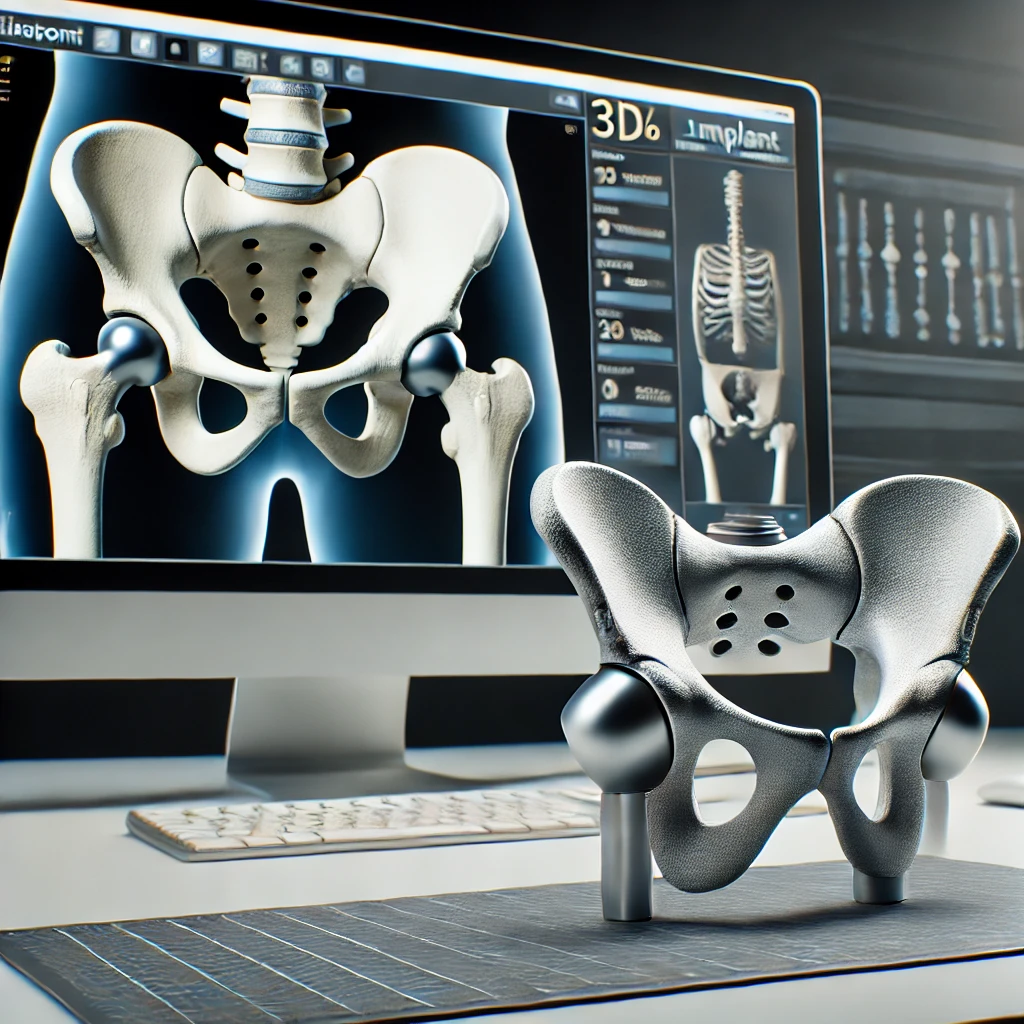
2. Custom Medical Devices and Implants
Another exciting application of 3D scanning in healthcare is the creation of custom medical devices and implants.
Traditional implants come in standard sizes, which can lead to complications if they don’t fit a patient perfectly. But with 3D scanning, doctors can create a digital model of the patient’s anatomy and design an implant that fits perfectly.
This is particularly useful in orthopedics, where custom-fitted joint replacements can significantly improve patient outcomes. It’s also being used in dentistry to create custom crowns, bridges, and dentures that fit more comfortably and function better.
3. Detailed Diagnostic Imaging
Volumetric scanning is changing the way we diagnose diseases. Traditional imaging techniques, like X-rays or MRIs, provide 2D slices of the body, which doctors then have to piece together mentally to get a full picture. Volumetric scanning, on the other hand, creates a complete 3D image, making it easier to spot abnormalities and diagnose conditions accurately.
For example, in cancer treatment, volumetric scans can be used to precisely locate tumors and determine their size and shape. This information is crucial for planning treatments like surgery or radiation therapy, where precision is key to targeting the tumor while sparing healthy tissue.
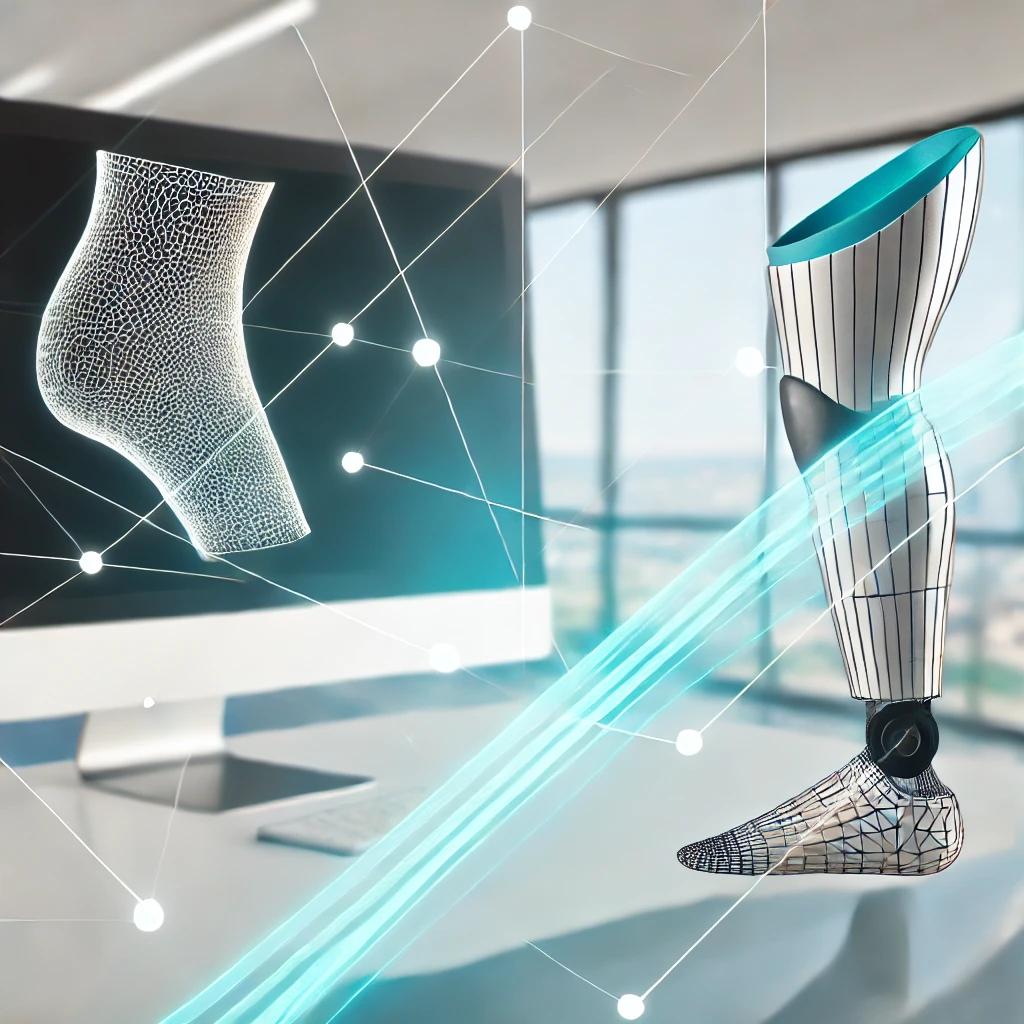
4. Patient-Specific Prosthetics
Prosthetics have come a long way, and 3D scanning is a big part of that evolution. By scanning a patient’s residual limb, doctors can create a prosthetic that fits perfectly, reducing discomfort and improving functionality. This is a game-changer for amputees, who often struggle with poorly fitting prosthetics that can cause pain and limit mobility.
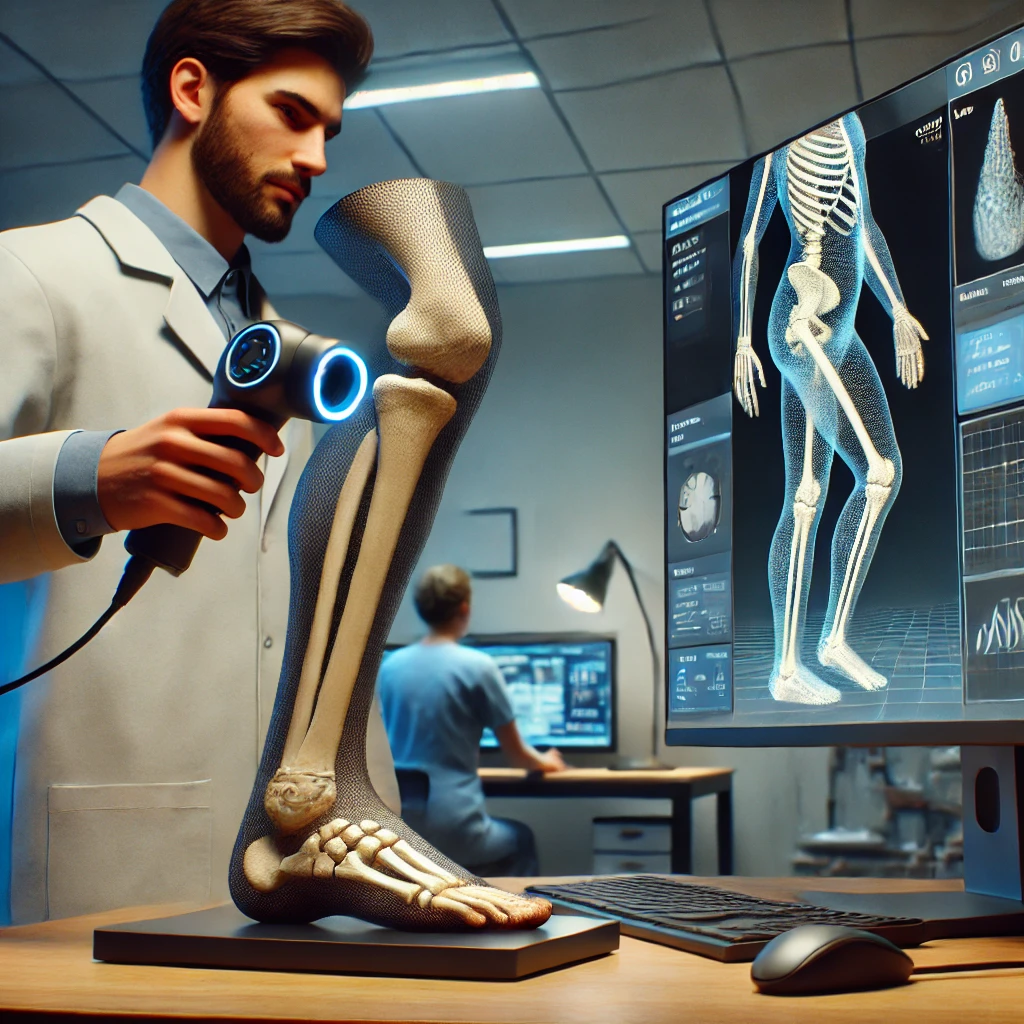

In addition to improving the fit, 3D scanning also speeds up the process of creating prosthetics, meaning patients can get their new limb faster and start rehabilitation sooner.
5. Advancements in Telemedicine and Remote Care
With the rise of telemedicine, 3D and volumetric scanning are opening new possibilities for remote care. For example, patients in remote areas can have a scan done locally, and the 3D images can be sent to specialists in other parts of the world for analysis. This allows patients to receive expert care without having to travel long distances.
Volumetric scanning also makes it easier for doctors to monitor chronic conditions over time. By comparing scans taken at different times, doctors can see how a disease is progressing and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
The Future of 3D and Volumetric Scanning in Healthcare
The potential of 3D and volumetric scanning in healthcare is just beginning to be realized. As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications, from personalized medicine to advanced robotic surgeries. The future of healthcare is becoming more precise, personalized, and effective—thanks in large part to 3D and volumetric scanning.
Conclusion
3D and volumetric scanning are transforming healthcare, making treatments more precise, diagnostics more accurate, and patient care more personalized. Whether it’s planning complex surgeries, creating custom implants, or improving telemedicine, these technologies are helping doctors provide better care and improve patient outcomes. As they continue to evolve, we can look forward to even more groundbreaking applications in the years to come.